Human Unigene
RZPD-3 Microarray -
a new tool for
functional analysis of the human genome
Groups of the EMBL and RZPD
produced a whole genome cDNA microarray. Based on the NCBI UniGene
clustering (
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Uni-Gene)
cDNA clones were selected from the Image clone collection representing
51.145 clusters.
The resulting Human
UnigeneSet-RZPD3 was selected according to the following criteria:
- More than one sequence per
cluster
- As close as possible to the 3'end
of the cDNA
- Length of the insert between 500
and 1200 bp
Of these clones 32.000 have been
sequence verified, characterization of further 20.000 clones is in progress.
cDNA inserts were PCR amplified, purified, and spotted on glass slides.
Analysis of PCR fragments on agarose gels, documentation, control DNAs
("spike-in controls") and Cy5- / Cy3-labeled Oligonucleotides on the
slides insure the quality of the microarray and reliability of hybridisation
results. Initial comparative hybridisations with RNA from human cell lines
demonstrate the potential of the new microarray in biomedical research.
Production
Process of the Microarray
PCR - cDNA inserts
were amplified with a pair of NH2-modified flanking universal primers.
Purification - The PCR
products were purified on a Biomek FX robot (Beckman) using the Macherey-Nagel Nucleospin kit based on a silica matrix. Since a stacker was
added to the robot, 4 x 96well PCR plates could be purified in one run, which
takes 90min.
 Quality control
Quality control - The purified fragments were analysed on a buffer free agarose gel system (RTR, Amersham/Pharmacia). Gels were loaded by a Biomek 2000 robot (Beckman). Two gels can be loaded in 30 min, one gel run takes 5 min.

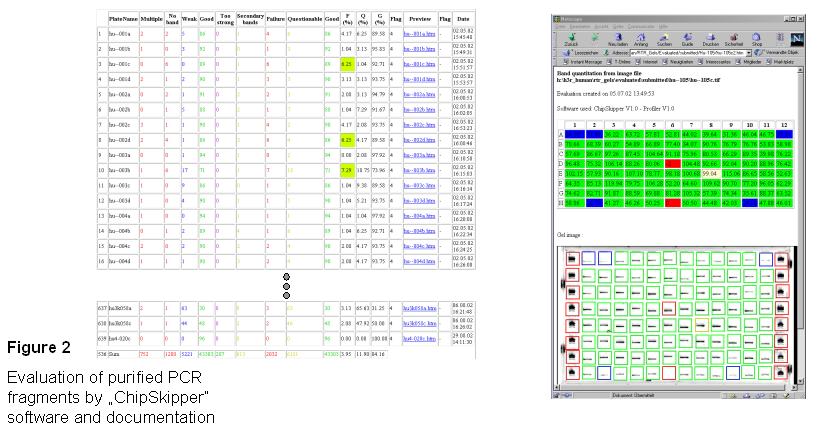
Evaluation and Documentation - Pictures of the Agarose gels were saved as tif-files and analysed with
ChipSkipper software, which allows a quantitative (concentration of DNA) and qualitative (multiple or single bands) evaluation of the purified PCR-fragments. The evaluated gel is saved as html-file connected to an access table containing the summary results of all gels analysed. The individual gel pictures can be activated from the summary table.
Single bands are quantified according the DNA marker. Missing or
multiple bands are marked with red boxes, weak bands with blue boxes.
Yellow boxes mark strong bands with a weaker second band.
Resulting gel pictures are saved as html-files.
A summary of each gel evaluation is stored in an acess table
(with a link to each gelpicture. Bottom line of the table shows the
final result of all gels with all PCR products purified.
As a result only 3,95% of the cDNA fragments could not be
amplified or showed multiple bands.
Preparation of spotting plates
- PCR products were transfered into 384 well microtiter plates in
2xSSC spotting buffer. By using a Biomek FX with a stacker 4 spotting plates
could be prepared in one run lasting 40 min.
Spotting - spotting is
performed on a GeneMachines OmniGrid spotter with 48 split needles on
amino-silane coated slides. One
representative of the clone set was spotted on two slides A and B, thus each
slide carries more than 26.000 spots including spiking controls and spotted
primers.
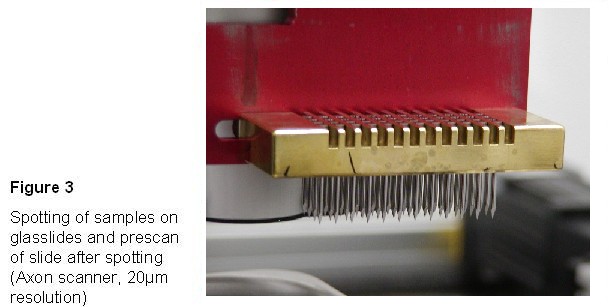
Slides were scanned with an
axon scanner (preview) after spotting and attachment, to control spotting
efficiency.
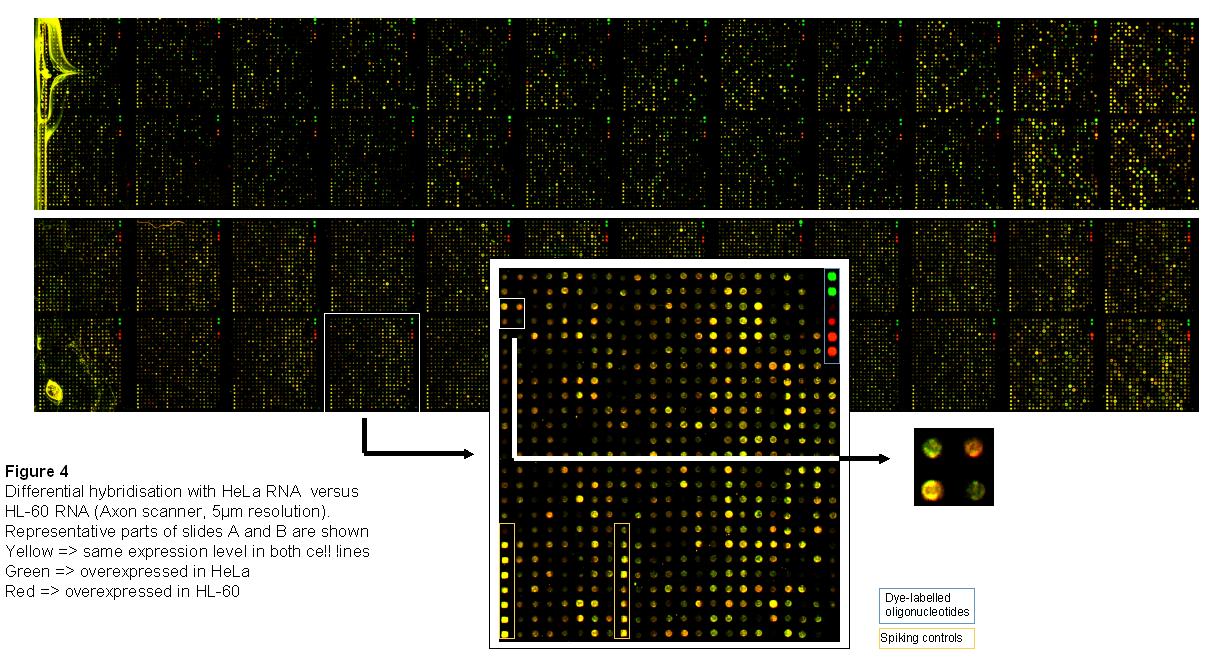
Complex
hybridization
n
Isolation of total RNA by standard procedure (Trizol method, PeqLab) from
human HeLa and HL-60 cells.
n
Direct labeling during cDNA synthesis and purification of probes (Qiagen
kit). Here: HeLa sample labeled with Cy3-dUTPs (green), HL-60
labeled with Cy5-dUTPs (red).
n
Complex hybrization on Human Unigene RZPD-3 Microarray (2 slides,
about 25.000 spots each): 5xSSC, 0.1% SDS, 42°C, 16h (Amersham
automated hybridization station).
n
Scanning of slides (Axon scanner, 5μm resolution)
n
Data analysis with different software tools (GenePix, Axon; ChipSkipper,
Christian Schwager, EMBL; Spotfire)
People involved :
Ute Wirkner1, Christian Maercker2, Mechthild
Wagner1, Heiko Drzonek1, Uwe Radelof3, Anja
Kellermann3, Johannes Maurer3, Christian
Schwager1, Bernhard
Korn2, Wilhelm Ansorge
1
DKFZ
Deutsche Krebsforschungszentrum,
INF360, Heidelberg, Germany
2
: rzpd
Deutsches Ressourcenzentrum
f¨ur Genomforschung GmbH
E-Mail:info@rzpd.de
maercker@rzpd.de
Acknowledgements
n
Jan Selig,
EMBL (Robotics)
n
Mona Kessler, Christine Schl¨osser, Christiane Rutenberg,
Susanne Hermann, RZPD (hybridizations, data analysis)
n
Frank Schwarz, Oliver Heil, Lars Ebert, Peter Neubert, Steffen
Schulze-
Kremer, Martin Holst, RZPD (bioinformatics, poster design)
n
Annemarie Poustka, DKFZ, Hans Lehrach, MPIMG (founder and
advisers of RZPD, array design, technology development)
n
Stefan Haas, Martin Vingron, MPIMG (cluster analysis)
n
Martin Stock, RZPD (administrative managing director)
n
BMBF (financial support)


 Quality control - The purified fragments were analysed on a buffer free agarose gel system (RTR, Amersham/Pharmacia). Gels were loaded by a Biomek 2000 robot (Beckman). Two gels can be loaded in 30 min, one gel run takes 5 min.
Quality control - The purified fragments were analysed on a buffer free agarose gel system (RTR, Amersham/Pharmacia). Gels were loaded by a Biomek 2000 robot (Beckman). Two gels can be loaded in 30 min, one gel run takes 5 min.