CS-Cal performs two fits:
Linear model:
SF = eα*Dose
In Radiology, this is the expected model for irradiation with HIGH Linear Energy Tranfer (LET) radiation/particles (e.g. Corbon/Oxygen ions).
Linear quadratic model:
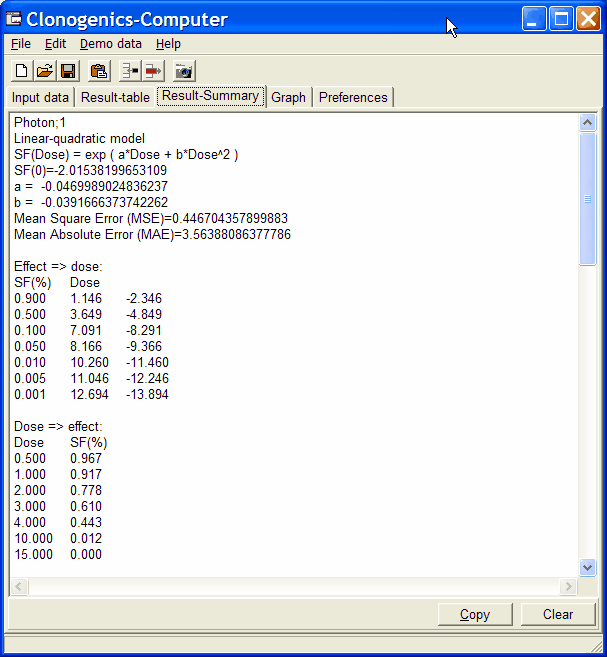
SF = eα*Dose + β*Dose2
In Radiology, this is the expected model for LOW Linear Energy Transfer (LET) irradiation (e.g. X-rays from Co60, Linear accelerators, ...).
Typically α and β are negative numbers.
In the Results summary tab you can see the parameters for the selected model:/p>

| SF(0) | Surviving Fraction computed with the corresponding regression model at dose=0 |
| α | Coefficient of the "linear" component in the regression model |
| β | Coefficient of the "quadratic" component in the regression model (in the "linaer" model b=0 by definition) |
| MSE | Mean Square Error = Sum of quadratic deviations between experimental data and
regression model. As smaller MSE as better describes the model measured experimental data. |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error = Sum of absolute deviations. |
| Effect=>Dose | Computed dose required to generate a certain SF effect: |
| 0.900 | The "dose" at which Surviving Fraction falls down to 90% For the linear-quadratic model two values are listed. Normally only one is meanigful. |
| 0.500 | The "dose" at which Surviving Fraction falls down to 50% |
| 0.100 | The "dose" at which Surviving Fraction falls down to 10% |
| .../td> | ... |
| Dose=>Effect | Computed SF effect generated by a predefined dose. |
| 0.500 | Resulting SF |
| 1.000 | Resulting SF |
| 2.000 | Resulting SF |
| ... | ... |
Select Main menu | Edit | Copyor blick the Copy button from tool bar
to copy formulas and parameters to clipboard.