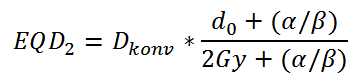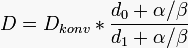 (1)
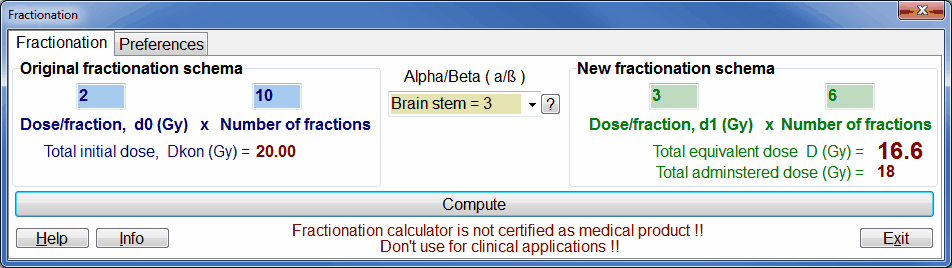
(1)| Dkonv | = original full dose (e.g. 30 Gy) |
| do | = original dose per fraction (e.g. 2 Gy) |
| d1 | = new required dose per fraction (e.g. 3 Gy) |
| α / β | = tissue dependent sensitivity factor (e.g. 3 for heart tissue) This α / β -value is the one, derived from the linear-quadratic model fit to clonogenic survival data |
| D | = resulting biological equivalent dose ( for the example: D=25) |